Page 56 - sjsi
P. 56
Research Article: Mahjoub et al 56
water quality (19) . As various types of gases (e.g.,
140
NH3, greenhouse gases, and H2S) are created
120 Milk from manure via microbial fermentation or
AA Conc. g/day 80 chemical changes, farm odor and a reduction in
100
Feed
air quality at stalls and during manure storage
60
(20)
40
is worth knowing that the amount of gas
20 before application to the field may occur . It
0 generated by manure is determined by both
internal and external factors. External
influences include chemical forms of nutrients
and nutrient concentrations, temperature,
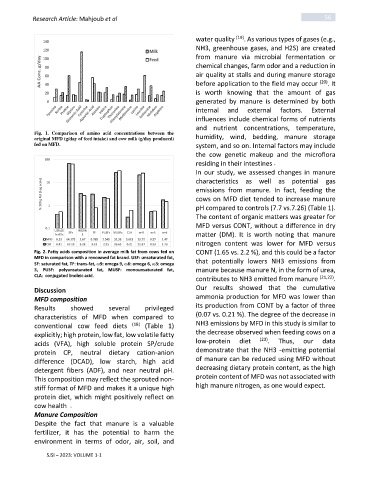
Fig. 1. Comparison of amino acid concentrations between the
original MFD (g/day of feed intake) and cow milk (g/day produced) humidity, wind, bedding, manure storage
fed on MFD. system, and so on. Internal factors may include
the cow genetic makeup and the microflora
100
residing in their intestines .
In our study, we assessed changes in manure
% 100 g Fat (Log scale) 1 emissions from manure. In fact, feeding the
characteristics as well as potential gas
10
cows on MFD diet tended to increase manure
pH compared to controls (7.7 vs.7.26) (Table 1).
The content of organic matters was greater for
MFD versus CONT, without a difference in dry
0.1
USFs/S SFs W6/W TF PUSFs MUSFs CLA w-9 w-3 w-6
Fs+TFs 3 matter (DM). It is worth noting that manure
MFD 0.53 64.175 2.67 0.785 2.045 32.38 0.615 25.72 0.57 1.47
Ctrl 0.41 67.18 3.28 3.13 2.25 26.65 0.31 21.37 0.53 1.73 nitrogen content was lower for MFD versus
Fig. 2. Fatty acids composition in average milk fat from cows fed on CONT (1.65 vs. 2.2 %), and this could be a factor
MFD in comparison with a renowned fat brand. USF: unsaturated fat, that potentially lowers NH3 emissions from
SF: saturated fat, TF: trans-fat, 9: omega 9, 6: omega 6, 3: omega
3, PUSF: polyunsaturated fat, MUSF: monounsaturated fat, manure because manure N, in the form of urea,
CLA: conjugated linoleic acid.
contributes to NH3 emitted from manure (21,22) .
Discussion Our results showed that the cumulative
MFD composition ammonia production for MFD was lower than
Results showed several privileged its production from CONT by a factor of three
(0.07 vs. 0.21 %). The degree of the decrease in
characteristics of MFD when compared to
conventional cow feed diets (18) (Table 1) NH3 emissions by MFD in this study is similar to
explicitly; high protein, low fat, low volatile fatty the decrease observed when feeding cows on a
low-protein diet (23) . Thus, our data
acids (VFA), high soluble protein SP/crude
protein CP, neutral dietary cation-anion demonstrate that the NH3 -emitting potential
difference (DCAD), low starch, high acid of manure can be reduced using MFD without
decreasing dietary protein content, as the high
detergent fibers (ADF), and near neutral pH.
This composition may reflect the sprouted non- protein content of MFD was not associated with
stiff format of MFD and makes it a unique high high manure nitrogen, as one would expect.
protein diet, which might positively reflect on
cow health .
Manure Composition
Despite the fact that manure is a valuable
fertilizer, it has the potential to harm the
environment in terms of odor, air, soil, and
SJSI – 2023: VOLUME 1-1