Page 57 - sjsi
P. 57
Research Article: Mahjoub et al 57
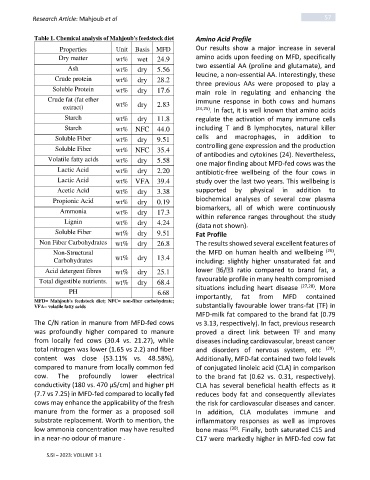
Table 1. Chemical analysis of Mahjoub's feedstock diet Amino Acid Profile
Properties Unit Basis MFD Our results show a major increase in several
Dry matter wt% wet 24.9 amino acids upon feeding on MFD, specifically
Ash wt% dry 5.56 two essential AA (proline and glutamate), and
Crude protein wt% dry 28.2 leucine, a non-essential AA. Interestingly, these
Soluble Protein wt% dry 17.6 three previous AAs were proposed to play a
main role in regulating and enhancing the
Crude fat (fat ether immune response in both cows and humans
extract) wt% dry 2.83 (24,25) . In fact, it is well known that amino acids
Starch wt% dry 11.8 regulate the activation of many immune cells
Starch wt% NFC 44.0 including T and B lymphocytes, natural killer
Soluble Fiber wt% dry 9.51 cells and macrophages, in addition to
Soluble Fiber wt% NFC 35.4 controlling gene expression and the production
Volatile fatty acids wt% dry 5.58 of antibodies and cytokines (24). Nevertheless,
one major finding about MFD-fed cows was the
Lactic Acid wt% dry 2.20 antibiotic-free wellbeing of the four cows in
Lactic Acid wt% VFA 39.4 study over the last two years. This wellbeing is
Acetic Acid wt% dry 3.38 supported by physical in addition to
Propionic Acid wt% dry 0.19 biochemical analyses of several cow plasma
Ammonia wt% dry 17.3 biomarkers, all of which were continuously
Lignin wt% dry 4.24 within reference ranges throughout the study
(data not shown) .
Soluble Fiber wt% dry 9.51 Fat Profile
Non Fiber Carbohydrates wt% dry 26.8 The results showed several excellent features of
Non-Structural the MFD on human health and wellbeing (26) ,
Carbohydrates wt% dry 13.4 including: slightly higher unsaturated fat and
Acid detergent fibres wt% dry 25.1 lower 6/ 3 ratio compared to brand fat, a
Total digestible nutrients. wt% dry 68.4 favourable profile in many health compromised
PH 6.68 situations including heart disease (27,28) . More
MFD= Mahjoub's feedstock diet; NFC= non-fiber carbohydrate; importantly, fat from MFD contained
VFA= volatile fatty acids substantially favourable lower trans-fat (TF) in
MFD-milk fat compared to the brand fat (0.79
The C/N ration in manure from MFD-fed cows vs 3.13, respectively). In fact, previous research
was profoundly higher compared to manure proved a direct link between TF and many
from locally fed cows (30.4 vs. 21.27), while diseases including cardiovascular, breast cancer
total nitrogen was lower (1.65 vs 2.2) and fiber and disorders of nervous system, etc (29) .
content was close (53.11% vs. 48.58%), Additionally, MFD-fat contained two fold levels
compared to manure from locally common fed of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) in comparison
cow. The profoundly lower electrical to the brand fat (0.62 vs. 0.31, respectively).
conductivity (180 vs. 470 μS/cm) and higher pH CLA has several beneficial health effects as it
(7.7 vs 7.25) in MFD-fed compared to locally fed reduces body fat and consequently alleviates
cows may enhance the applicability of the fresh the risk for cardiovascular diseases and cancer.
manure from the former as a proposed soil In addition, CLA modulates immune and
substrate replacement. Worth to mention, the inflammatory responses as well as improves
low ammonia concentration may have resulted bone mass (30) . Finally, both saturated C15 and
in a near-no odour of manure . C17 were markedly higher in MFD-fed cow fat
SJSI – 2023: VOLUME 1-1